Dynamic Programming with Bitmasks LIVE Webinar [Hinglish] - by Prateek Narang, Coding Blocks
In this webinar, we are going to learn advanced dynamic programming using Bitmasking. The following problems will be discussed.
Little Elephant and T-Shirts
Problem Statement
Little Elephant and his friends are going to a party. Each person has his own collection of T-Shirts. There are 100 different kind of T-Shirts. Each T-Shirt has a unique id between 1 and 100. No person has two T-Shirts of the same ID. They want to know how many arrangements are there in which no two persons wear same T-Shirt One arrangement is considered different from another arrangement if there is at least one person wearing a different kind of T-Shirt in another arrangement.
Sample Input
3
5 100 1
2
5 100
Output
4
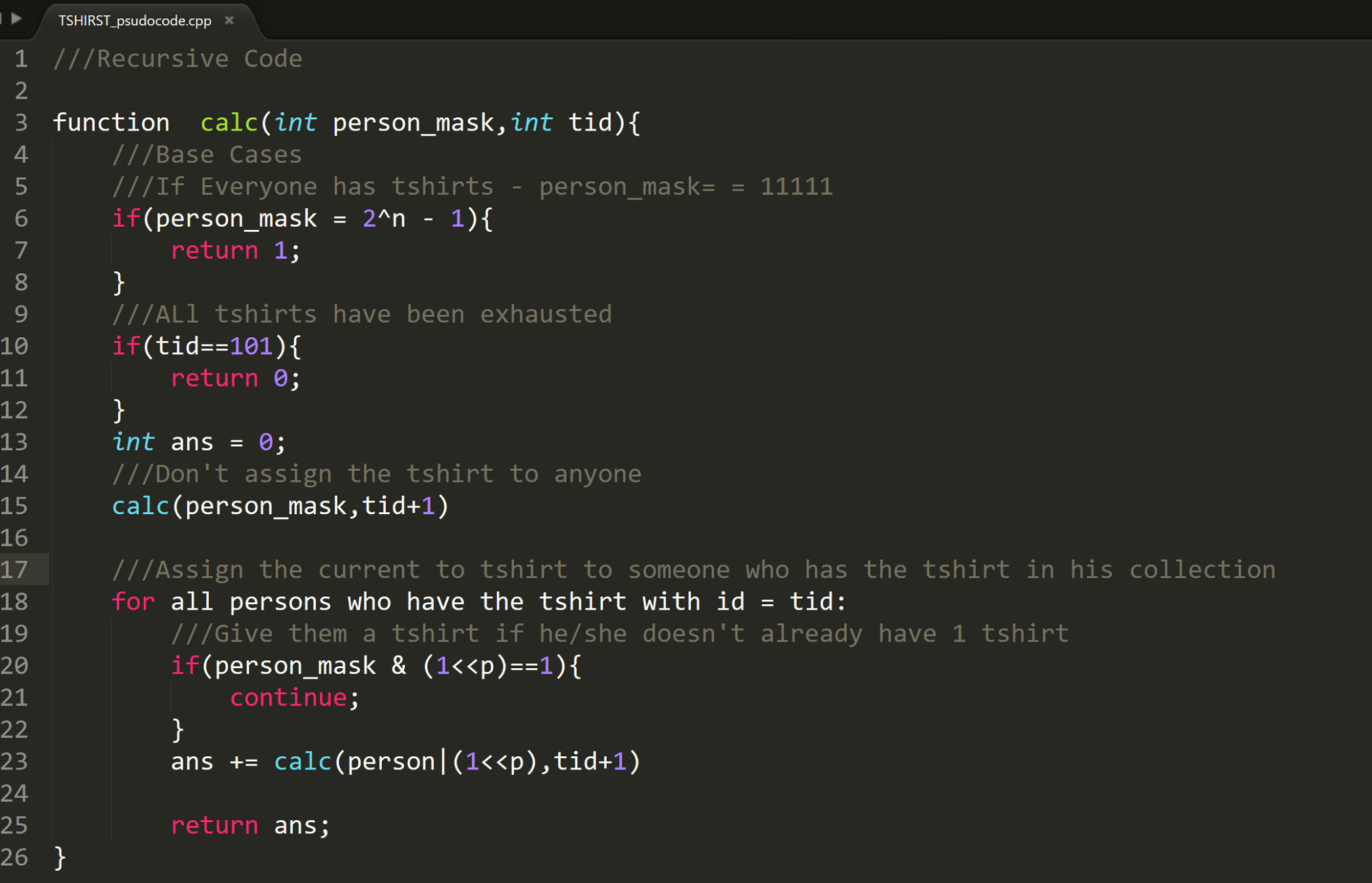
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define MOD 1000000007
#define DEBUG false
int stoi(string &s){
stringstream ss(s);
int x;
ss>>x;
return x;
}
int ALL_PERSON;
ll dp[1025][102];
vector<vector<int> > v;
///mask denotes set of people who have got the t-shirts(unique)
///tid the current t-shirt we are going to give to some person who has this tshirt in almirah
ll calc(int mask,int tid){
if(mask==ALL_PERSON){
return 1;
}
///ALl tshirts exhausted
if(tid==101){
return 0;
}
if(dp[mask][tid]!=-1){
return dp[mask][tid];
}
ll ans = 0;
///Current tid is not alloted to anyone ( more tshirts less people )
ans = calc(mask,tid+1);
///Allot the current to tshirt to someone who has that tshirt in almirah, but is not given a tshirt yet
for(int p:v[tid]){
if((mask&(1<<p))==0){
ans += calc((mask|(1<<p)),tid+1);
}
}
ans %= MOD;
dp[mask][tid] = ans;
return ans;
}
int main(){
v.reserve(110);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
int n;
cin>>n;
ALL_PERSON = (1<<n) - 1;
string s;
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++){
v[i].clear();
}
cin.get();
///Created the Reverse Mapping from the input
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
getline(cin,s);
stringstream ss(s);
string temp;
while(ss>>temp){
v[stoi(temp)].push_back(i);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++){
sort(v[i].begin(),v[i].end());
if(v[i].size()>0 && DEBUG){
cout<<"T-Shirt "<<i<<" -> ";
for(auto j:v[i]){
cout<<j+1<<",";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
cout<<calc(0,1)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
N-Queen Problem ( Backtracking + Bitmasking ) - World’s Most Optimized Approach
Problem Statement
Given a N X N chessboard you have to count the number of possible Valid configurations to place N Queens on the chessboard such that no queen cuts each other. 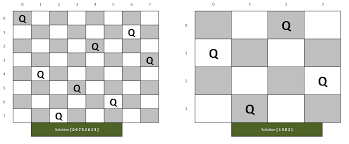
Possible Approaches
- Normal Backtracking with isSafe Function = Least efficient
- Backtracking + Bitsets
- Backtracking + Bitmasks = WORLD’s MOST EFFICIENT SOLUTION
We are going to discuss the third approach !!!
Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
int ans =0, DONE;
///rowmask denote which positions(colms) in all rows are filled
/// ld, rd denotes unsafe positions along diagonals for the current row
/// done is vector of all 11111 ( n times 1 )
/// safe denotes the cols which are safe in the current row
/// Most optimisized n queen code !
void solve(int rowMask,int ld,int rd){
if(rowMask==DONE){ ans++; return; }
int safe = DONE&(~(rowMask|ld|rd));
while(safe){
int p = safe &(-safe);
safe = safe - p;
solve(rowMask|p, (ld|p)<<1, (rd|p)>>1);
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
DONE = ((1<<n) - 1);
solve(0,0,0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
Travelling Salesman Problem - Shortest Code using Bitmasks
Problem Statement
Given n cities and their pairwise distances in the form of matrix(adjacency matrix) of size n X n compute the min cost of making a Hamiltonian Tour. Hamiltonian Tour - A tour which starts from any city s goes through all the n - 1 cities exactly once, and returns to starting city s.
Application: Amazon Delivery Van Route.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n=4;
int dist[10][10] = {
{0,20,42,25},
{20,0,30,34},
{42,30,0,10},
{25,34,10,0}
};
int tsp(int pos,int mask){
if(mask==((1<<n)-1)){
///All cities have been visited
return dist[pos][0];
}
int ans = 2000;
///Try to go to all other cities
for(int nextCity=0;nextCity<4;nextCity++){
if(((mask&(1<<nextCity))==0)){
ans = min(ans,dist[pos][nextCity]+ tsp(nextCity, mask|(1<<nextCity)));
}
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
cout<<tsp(0,1)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Bear and Shop Trip ( SHOPTRIP )
Problem Statement
There are n shops, i-th of which is located at the coordinates (xi,yi) . There are k ingredients numbered from 1 to k. Each shop contains some of these ingredients, which is given by a binary string si of k characters. If s[i][j]=1, then it means that j-th ingredient is present in i-th shop. You want to collect all the k ingredients by visiting some shops starting from coordinates (0,0) and finishing your journey by coming at (0,0) again. You want to travel the least possible distance in this journey. Find out the least distance of your journey to collect all the ingredients. If it is not possible to collect all the ingredients, output -1. 
Thank you for Reading !
Keep Coding, Keep Building !